Defects of Steel
Defects of Steel
Several types of defects can be found in steel, including:
- Inclusions: These are non-metallic particles that are present in the steel, such as slag, oxides, and other impurities. These particles can cause weakness in the steel and can also affect its surface finish.
- Porosity: This phenomenon is the presence of small holes or voids within the steel. Porosity can occur due to improper casting techniques, and it can also cause weakness in the steel.
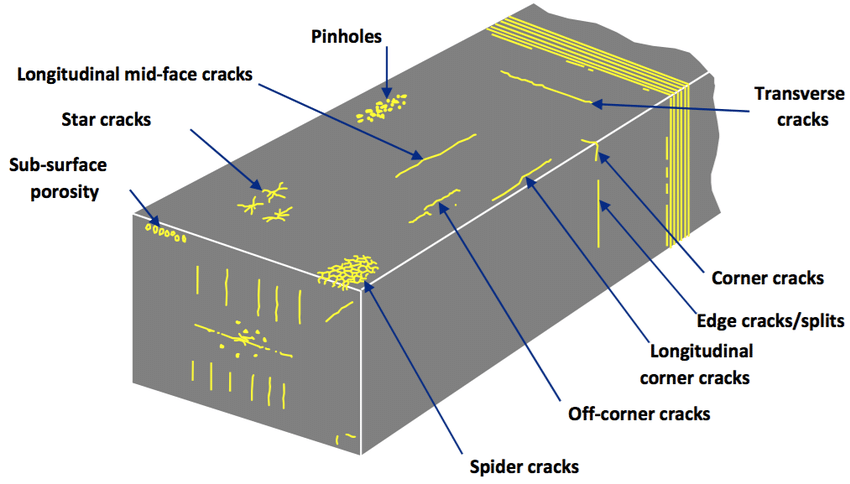
- Cracks: Cracks can occur in steel due to various factors, including improper heat treatment, welding, and mechanical stress. They can weaken the steel and make it more susceptible to failure.
- Laminations: These are layers of steel that have separated from one another, creating a layered structure. Laminations can occur due to improper rolling or forging techniques, and they can also cause weakness in the steel.
- Seam: These are surface defects that occur due to improper welding or casting. They appear as lines on the surface of the steel and can weaken it.
- Scabs: These are raised or depressed areas on the surface of the steel that is caused by improper rolling or forging. They can weaken the steel and affect its surface finish.
- Laps: A lap is a type of surface defect that occurs when two layers of steel overlap one another, causing a raised area on the surface. Laps can weaken the steel and affect its surface finish.
- Cold Shut: A cold shut is a type of defect that occurs when two streams of molten steel do not fuse together properly during casting, resulting in a partial fusion. They can weaken the steel and affect its surface finish.
Steel can exhibit a variety of defects. It is important to detect and remove these defects during the manufacturing process to ensure the integrity and quality of the steel.
Further readings.
Kindly contact Apurv Gupta with your requirements on +91 9004064570 or email at apurv@ambhe.com.
Some lesser known Defects of Steel
1. Lamellar Tearing
Lamellar tearing is a rare but critical defect that occurs in welded steel plates, especially those with high sulfur content.

- Inclusion of non-metallic materials (like manganese sulfide) aligned parallel to the rolling plane.
- Poor through-thickness ductility.

- Creates subsurface cracks during welding.
- Reduces load-bearing capacity, especially in thick plates.

- Use steel with low sulphur content.
- Apply welding techniques that minimise through-thickness stress.
- Consider Z-quality steel plates.
2. Segregation Bands
Segregation bands are uneven distributions of alloying elements visible in rolled steel sections.

- Uneven cooling during solidification leads to concentration differences in carbon, manganese, and phosphorus.

- Causes inconsistent mechanical properties across a steel section.
- Weak points may form under cyclic loads.

- Improve ingot casting and cooling control.
- Use secondary refining techniques.
3. Hydrogen Flaking (Flakes)
Also known as fish-eye defects, hydrogen flakes are tiny internal cracks caused by trapped hydrogen.

- High hydrogen levels during steelmaking.
- Rapid cooling after forging.

- Reduced toughness.
- Risk of sudden brittle failure.

- Vacuum degassing to remove hydrogen.
- Controlled cooling rates.
4. Banded Structure
This occurs when steel grains align into bands due to rolling in one direction.

- Segregation of pearlite and ferrite during hot rolling.
- Incomplete homogenization.

- Unequal tensile properties along different directions (anisotropy).
- Reduced fatigue life.

- Controlled rolling and heat treatment.
- Avoid excessive cold work.
5. Pipe Defect
A pipe defect is a central cavity in ingots, often unnoticed until machining.

- Solidification shrinkage during ingot casting.

- Weakens structural integrity after machining.
- Increases scrap rates.

- Controlled feeding during casting.
- Use of hot tops and risers.